Electrical vehicle mechanism
An Electric Vehicle (EV) works using a battery instead of a fuel engine. Here’s how it functions in simple terms:
- Battery – The EV stores energy in a rechargeable battery (like a bigger version of a mobile phone battery).
- Electric Motor – The battery sends electricity to an electric motor, which turns the wheels.
- Controller – A controller acts as the brain of the car, deciding how much power to send to the motor based on how much you press the accelerator.
- Charging – Instead of filling up with petrol, you plug the car into a charger to recharge the battery.
- Regenerative Braking – When you apply brakes, the car converts some of the lost energy back into the battery, improving efficiency.
Since there’s no fuel engine, EVs are quieter, require less maintenance, and don’t produce pollution while driving.
Focus here for working:
- Battery stores power – Just like a phone, the EV has a big battery that stores electricity.
- Motor moves the car – The battery sends power to an electric motor, which turns the wheels.
- No fuel needed – Instead of petrol or diesel, you charge the battery by plugging it into an electric socket or charging station.
- Smooth and quiet – Since there’s no fuel engine, EVs make less noise and run smoothly.
- Recycles energy – When you brake, the car captures some of the lost energy and reuses it, making the battery last longer.
EVs are eco-friendly, require less maintenance, and are the future of clean transportation!
AI in electric vehicles (EVs) makes them smarter and more efficient. Here’s how it helps:
- Smart Battery Management – AI predicts how much battery is left, finds the best way to save energy, and improves charging speed.
- Self-Driving Features – AI helps EVs detect roads, traffic, and obstacles for auto-driving and safer assistance (like Tesla’s Autopilot).
- Predictive Maintenance – AI warns about possible issues before they happen, reducing breakdowns.
- Route Optimization – AI suggests the best and shortest routes, saving battery and time.
- Driver Assistance – AI provides features like voice commands, automatic parking, and lane-keeping for easier driving.
AI makes EVs more efficient, safer, and user-friendly, pushing us closer to the future of smart transportation!
What’s trending in electrical vehicles ?
Here are some new innovations in electric vehicles (EVs) explained simply:
- Faster Charging – New batteries can charge in minutes instead of hours, making EVs more convenient.
- Longer Battery Life – Solid-state batteries last longer, store more power, and charge faster than regular ones.
- Wireless Charging – Some EVs can charge without plugging in, just by parking over a special charging pad.
- Solar-Powered EVs – Cars like the Lightyear 0 have solar panels to charge while driving, reducing the need for frequent charging.
- Self-Driving Technology – AI is improving autonomous driving, making EVs smarter and safer.
- Battery Swapping – Instead of waiting for a charge, some companies offer quick battery swaps, like changing a phone battery.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Tech – EVs can now send power back to homes or the grid, helping during power cuts.
These innovations are making EVs faster, smarter, and more efficient, bringing us closer to a future of clean and convenient transportation!
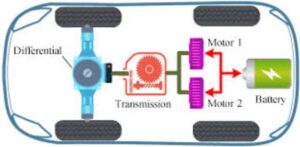
which motor is used in electrical vehicle ?

In electric vehicles (EVs), two main types of motors are used:
- AC Induction Motor – This motor works by using alternating current (AC) to generate magnetic fields that make the rotor (part that spins) turn. It’s simple, reliable, and doesn’t require permanent magnets. Many EVs, like older Tesla models, use this motor.
- Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) – This motor uses permanent magnets to create a stronger magnetic field. It’s more efficient and commonly used in newer EVs because it provides better performance and range. Many modern electric cars (like those from BMW and Nissan) use PMSMs.
Both motors are quiet, efficient, and powerful enough to drive the vehicle without the need for traditional fuel engines.
